 FREE SHIPPING on US orders over $150. Need help? Contact Us
FREE SHIPPING on US orders over $150. Need help? Contact Us The Four C's of a Diamond: Color, Clarity, Cut and Carat weight
Diamonds professionals use the following four factors to describe and classify diamonds: color, clarity, cut and carat weight. When taken together, they help in evaluating the finished diamonds you buy. That's why they are often called value factors.
Color
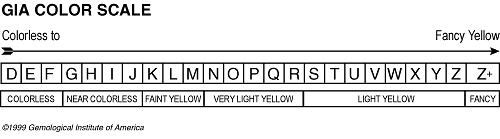

Diamonds in the normal color range are graded by their relative lack of color. A diamond that is said to have "fine color" has little or no visible coloration. The less color, the higher the value. Diamonds outside the normal color range are called fancy-colored and come in about any color you can imagine.

top
Clarity
Diamonds have internal features, called inclusions, and surface irregularities, called blemishes. Together, they’re called clarity characteristics. Clarity is the relative absence of clarity characteristics. Blemishes include scratches and nicks on a diamond’s surface. Inclusions are on the inside (some might break the surface of the stone, but they are still considered inclusions). Sometimes, tiny diamond or other mineral crystals are trapped inside a diamond when it forms. Depending on where they’re located, they might still be there after the stone has been cut and polished.
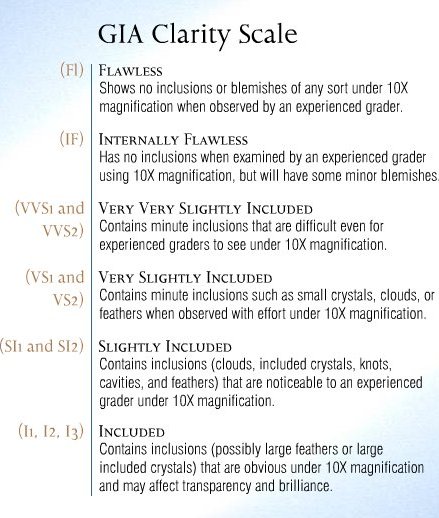
top
Cut
When looking for diamonds you may come across the terms, "Single Cut,” “Old Mine Cut” or “European Cut.” Single cut diamonds have a total of 17 facets. Most other designs have 58 facets.
Single cut diamonds are usually used on small accent stones and they won’t have the brilliance of a full cut diamond.
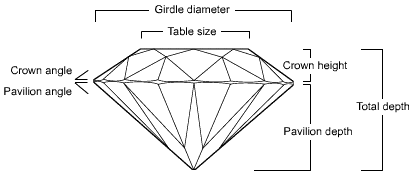
The cut of a diamond as a value factor, refers to its proportions, symmetry and finish. It is not to be confused with its shape.
Proportion refers to the angles and relative measurements of a polished diamond. More than any other feature, proportions determine a diamond's optical properties. Studies have shown that table size, crown angle, and pavilion depth have a dramatic effect on a diamond's appearance.
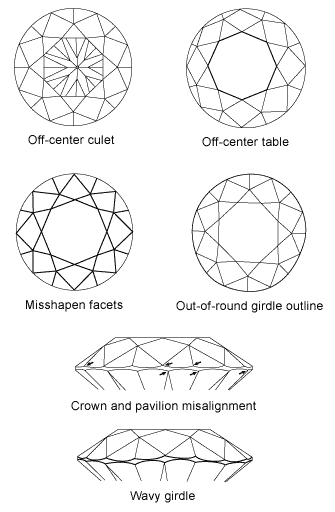
Symmetry is a grading term for the exactness of shape and placement of facets. Variations in symmetry include off-center culets and tables, poor facet alignment, misshapen facets, out-of-round girdles, and wavy girdles.
The finish is the quality of a diamond’s polish, the condition of its girdle, and the precision of the cut.
Diamond Shapes
Shapes other than the standard round brilliant shown above are called fancy shapes or fancy cuts. Their names are based on their shapes. The best known are the heart, marquise, pear-shaped cut, emerald-cut, oval, and radiant.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Round
|
Emerald
|
Princess
|
Radiant
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Marquise
|
Asscher
|
Briolette
|
Straight
Baguette |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Oval | Heart | Pear | Triangle |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Tapered Baguette |
Cushion | Half Moon | Trapezoid |
Click here to see larger pictures of diamonds.
Carat Weight
Diamonds are weighed to a thousandth (0.001) of a carat and then rounded to the nearest hundredth, or point. Over a carat, diamond weights are usually expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.03 ct. stone, for example, would be described as "one point oh three carats," or "one oh three." A diamond that weighs 0.83 ct. is said to weigh "eighty-three points," or an "eighty-three pointer." According to the 1907 international standard, one carat is equivalent to 0.2 gram.
The cumulative diamond weight of a piece of jewelry that includes several diamonds is measured in TCW (total carat weight) or pttw (points total weight) or Carats Total Weight (Carat TW). One TCW/Carat TW is equal to 100 pttw. For example, a diamond pendant with 83 pttw dia will have a total diamond weight of 0.83 carat or 0.83 TCW/Carat TW.
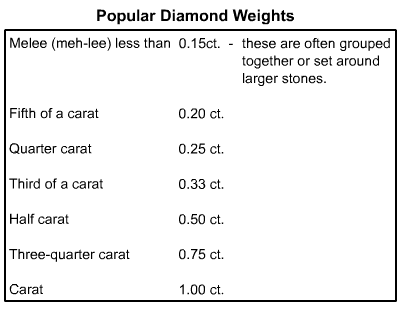
Some weights are considered "magic sizes" – half carat, three-quarter carat, carat. Visually, there’s little difference between a 0.99 ct. diamond and one that weighs a full carat. But the price differences between the two can be significant.
Many people would like to understand carat sizes in real terms. Here are some approximate, sample carat-weight to diameter-widths for Round* cut diamonds in popular sizes:
0.25 carat = 4.1 mm 0.50 carat = 5.2 mm
0.75 carat = 5.8 mm 1.00 carat = 6.5 mm
*Click here for Pear, Marquise, Oval, Emerald, Heart, Trillion & Princess mm to carats conversion chart or download and print PDF file (requires Adobe Acrobat Reader).
PS. Stone sizes are approximate. These charts are used for quick reference only. Stones should always be measured and/or weighed for accuracy.
|
Carats
|
Diameter (mm)
|
Carats |
Diameter (mm)
|
|
.005
|
1.0
|
1.25
|
7.0
|
|
.0067
|
1.15
|
1.33
|
7.2
|
|
.01
|
1.3
|
1.50
|
7.4
|
|
.015
|
1.5
|
1.60
|
7.6
|
|
.02
|
1.7
|
1.75
|
7.8
|
|
.025
|
1.8
|
1.90
|
8.0
|
|
.03
|
2.0
|
2.00
|
8.2
|
|
.035
|
2.1
|
2.15
|
8.4
|
|
.04
|
2.2
|
2.25
|
8.6
|
|
.05
|
2.4
|
2.50
|
8.8
|
|
.06
|
2.5
|
2.65
|
9.0
|
|
.07
|
2.7
|
2.85
|
9.2
|
|
.08
|
2.8
|
3.00
|
9.4
|
|
.09
|
2.9
|
3.15
|
9.6
|
|
.10
|
3.0
|
3.35
|
9.8
|
|
.11
|
3.1
|
3.50
|
10.0
|
|
.12
|
3.2
|
3.75
|
10.2
|
|
.14
|
3.3
|
4.00
|
10.4
|
|
.15
|
3.4
|
4.25
|
10.6
|
|
.16
|
3.5
|
4.50
|
10.8
|
|
.17
|
3.6
|
4.75
|
11.0
|
|
.18
|
3.7
|
5.00
|
11.2
|
|
.20
|
3.8
|
5.25
|
11.4
|
|
.22
|
3.9
|
5.50
|
11.6
|
|
.23
|
4.0
|
5.75
|
11.75
|
|
.25
|
4.1
|
5.81
|
11.8
|
|
.30
|
4.2
|
6.00
|
11.9
|
|
.33
|
4.4
|
6.25
|
12.1
|
|
.35
|
4.5
|
7.00
|
12.5
|
|
.38
|
4.6
|
7.50
|
12.85
|
|
.40
|
4.8
|
7.75
|
13.00
|
|
.43
|
4.9
|
8.00
|
13.1
|
|
.47
|
5.0
|
8.23
|
13.25
|
|
.50
|
5.2
|
8.50
|
13.4
|
|
.60
|
5.4
|
8.75
|
13.5
|
|
.63
|
5.5
|
9.00
|
13.65
|
|
.65
|
5.6
|
9.20
|
13.75
|
|
.75
|
5.8
|
9.75
|
14.0
|
|
.80
|
6.0
|
10.34
|
14.5
|
|
.85
|
6.2
|
12.00
|
15.0
|
|
.95
|
6.4
|
12.92
|
15.4
|
|
1.00
|
6.5
|
13.17
|
15.5
|
|
1.10
|
6.6
|
14.50
|
16.0
|
|
1.17
|
6.8
|
|
|



